
|
|
|
Health Freedom Resources

|
Can You Get Enough Omega-3 From Eating Fish?Possibly. If you eat the fish shown on this chart weekly, which are high in the Omega 3s EPA and DHA, you might! Recommendations while vary widely, with an average of 250-500 mg per day called for by many public health organizations, and 2,000 to 4,000 mg per day is recommended by the WHO and some studies for additional health benefits. * [1, 2, 3] 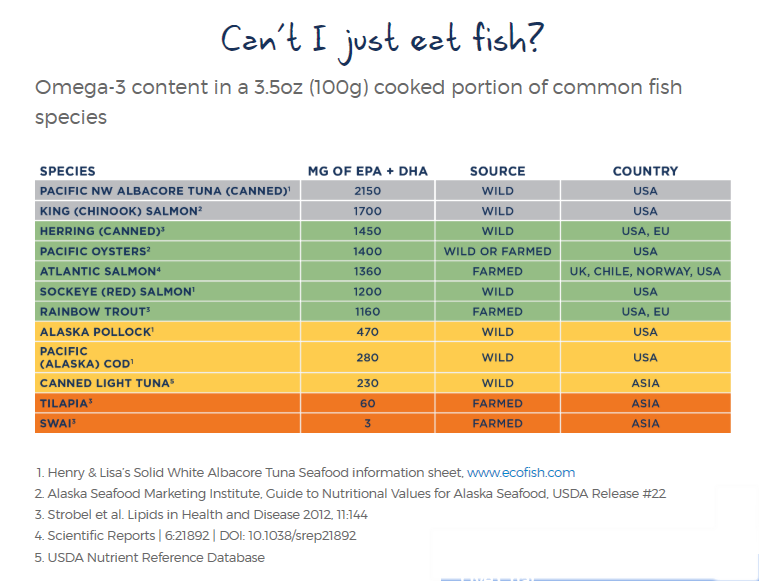
Historically, seafood used to be a much larger part of our diet, but most Americans no longer regularly eat much seafood. In 2018, Americans ate an average 219 lbs of red meat and poultry per person, but only about 16 lbs of seafood. What seafood Americans do eat is mostly imported farmed shrimp, accounting for nearly 25% of our seafood meals in a year. Farmed shrimp has very little Omega-3 content, and may not be grown with ethical labor practices, or may be tainted with antibiotics illegal for U.S. use. Many people limit the amount of fish they eat because of mercury contamination, especially from large fish like tuna. We recommend consumers make nutritious seafood choices. It is important to pay attention to the species and the country of origin of seafood you do eat, as well as the brand and traceability, because there is a large variation in Omega-3 content in seafood species and a potential for contamination. We believe you should eat fresh, non-contaminated seafood whenever possible, and take fresh fish oil supplements to ensure you get your optimal intake of Omega-3s. The oil of Alaskan Pollock (a food fish similar to Cod) is a rich natural source of EPA and DHA Omega-3s with about 20-25% natural Omega-3 fat content. The Omega-3 fatty acids of this Wild Alaskan Fish Oil has been concentrated with a sophisticated and proprietary AlaskOmega® process and can reach as high as 85%, so you can get a serving with the daily recommended intakes in just 1-2 capsules. What are the benefits of adequate Omega-3 fatty acids?
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any diseases. Reference list of studies on some of the benefits of fish oil and Omega-3 EPA and DHA fatty acids.Omega-3 fatty acids are among the world's most comprehensively studied nutrients. They have been shown to have numerous functions essential to health. The following studies are given for educational purposes only. We are not making any medical claims for products we sell. There are numerous studies from PubMed/National Institute of Health website database that were not included because Omega 3 fatty acids were studied in relation to disease. Any Omega 3 containing product we sell is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. If you have a medical condition, please work with your healthcare practitioner. Essential fatty acids, DHA and human brain, Meharban Singh, 2005 Mar;72(3):239-42.
Omega-3 supplementation lowers inflammation in healthy middle-aged and older adults: a randomized controlled trial, Health benefits of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), L A Horrocks 1, Y K Yeo, 10.1006/phrs.1999.0495 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10479465/ Docosahexaenoic acid is the preferred dietary n-3 fatty acid for the development of the brain and retina, G J Anderson 1, W E Connor, J D Corliss, 1990 Jan;27(1):89-97. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199001000-00023. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2136947/ Prenatal fatty acid status and immune development: the pathways and the evidence Susan L Prescott 1, Janet A Dunstan 2007 Sep;42(9):801-10. doi: 10.1007/s11745-007-3030-z. Epub 2007 Mar 13. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17952480/ An update on adding docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and arachidonic acid (AA) to baby formula Emily K K Tai 1, Xiao Bo Wang, Zhen-Yu Chen, 2013 Dec;4(12):1767-75. doi: 10.1039/c3fo60298b. Epub 2013 Oct 22. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24150114/ Maternal supplementation with very-long-chain n-3 fatty acids during pregnancy and lactation augments children's IQ at 4 years of age, Ingrid B Helland 1, Lars Smith, Kristin Saarem, Ola D Saugstad, Christian A Drevon, 2003 Jan;111(1):e39-44. doi: 10.1542/peds.111.1.e39. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12509593/ Maternal consumption of a docosahexaenoic acid-containing functional food during pregnancy: benefit for infant performance on problem-solving but not on recognition memory tasks at age 9 mo Michelle P Judge 1, Ofer Harel, Carol J Lammi-Keefe, 2007 Jun;85(6):1572-7. doi: 0.1093/ajcn/85.6.1572. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17556695/ Menstrual pain in Danish women correlated with low n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake, B Deutch, 1995 Jul;49(7):508-16. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7588501/ The impact of diet on anti-social, violent and criminal behavior, David Benton, 2007;31(5):752-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.02.002. Epub 2007 Mar 4. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17433442/
1. WHO. https://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/FFA_summary_rec_conclusion.pdf?ua=1 See our 10 different types of Wild Alaskan Fish Oil |
||
Copyright 2009-2026 Southern Botanicals Herbals & Nutrition, Inc
Southern Botanicals Herbals & Nutrition
611 S Myrtle Ave # D, Clearwater, FL 33756
(727) 443-7711

![]()